The poinsettia plant is a ubiquitous Christmas staple.

Every year, just after Thanksgiving, it emerges en masse at nurseries, big-box retailers, fundraisers, and holiday parties.
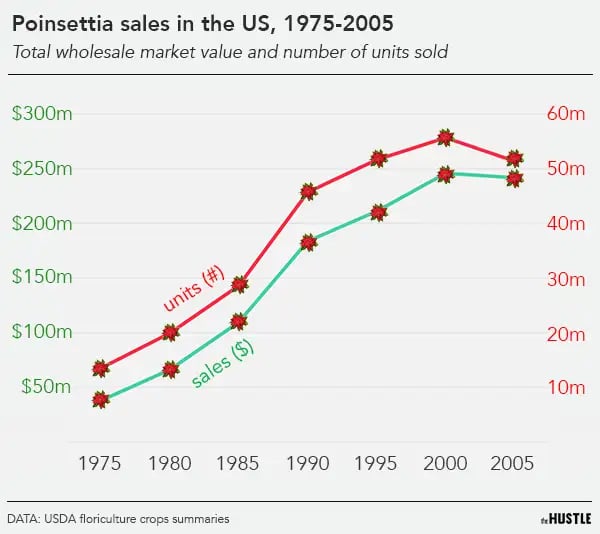
It’s one of the most popular plants in the world, with annual sales of ~90m units and a global retail impact of nearly $1B.
But behind the beautiful, blood-red bracts of the poinsettia, there’s a story rife with geopolitics, patent wars, a dethroned monopoly, and complex supply chains.
How did this Mexican shrub become America’s best-selling holiday plant?
To find out, The Hustle talked to poinsettia growers, breeders, salespeople, and historians.
Deep roots
Indigenous to Southern Mexico, the poinsettia (or cuetlaxochitl) was first used by 14th-century Nahua people for dye and medicinal purposes.
The plant’s brilliant red bracts — which are leaves, not flowers — were so revered by the Aztec emperor Montezuma that thousands of them were transported to the high-altitude capital of Tenochtitlan each winter.
After Spain colonized Mexico, Franciscan monks dubbed the plant flor de Nochebuena (“Flower of the Blessed Night”) and began to showcase it in annual Christmas processions.
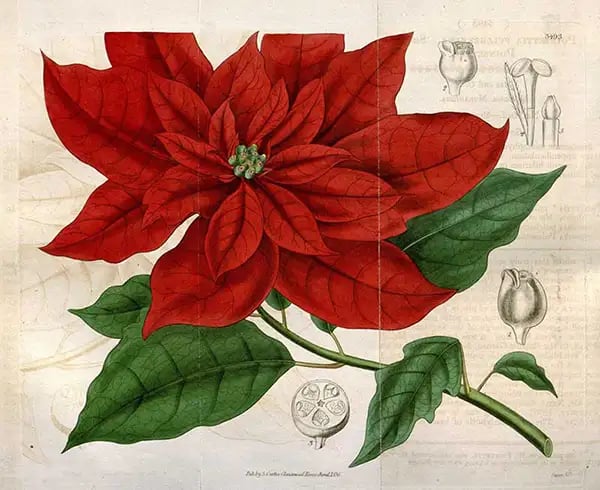
One of the first-known taxonomic illustrations of the poinsettia (Curtis’s Botanical Magazine v.63; 1836)
For the next few centuries, the plant was cultivated and celebrated in Mexico — yet it remained obscure to the rest of the world.
Then, along came Joel Poinsett.
Poinsett, a wealthy Southern Unionist and slave owner, was appointed as the first US minister to Mexico.
While there, he failed in an attempt to purchase Texas and became a persona non grata for meddling in the country’s internal affairs.
But on a trip to the Southern town of Taxco in 1828, just before he was he recalled, he encountered the flor de Nochebuena and was so struck by it that he shipped specimens back to the US.
The plant — which eventually became known to Westerners as the “poinsettia” — made its public American debut at a flower show in Philadelphia and quickly became the talk of the town.
In news reports at the time, it was described as “the showiest flower to yet be seen” and praised for having “the most brilliant scarlet [leaves] ]ever produced in the vegetable or mineral kingdom.”
By the end of the 19th century, nurserymen were growing and distributing poinsettias for ~$0.25 ($8 today) at local markets.
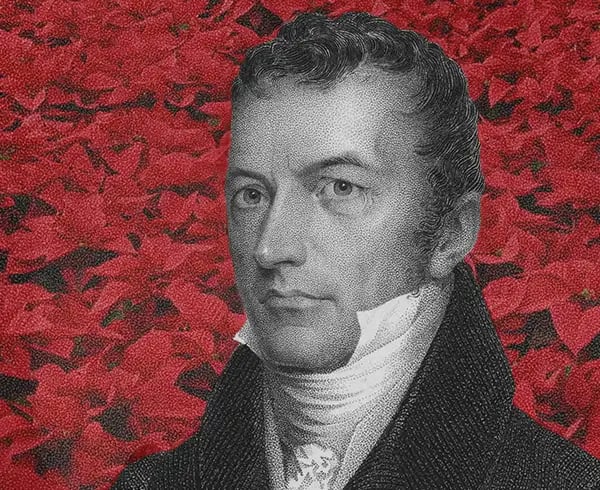

Joel Roberts Poinsett (Library of Congress, Charles Fenderich; photo illustration by The Hustle)
But several things worked against the poinsettia as a commercial entity.
“Perhaps no other plant or flower we handle… is short-lived, wilts quicker, or is more disappointing to those who receive it,” wrote Fritz Bahr, an early floriculturist.
The plant would only last 2-3 days — and its weak disposition meant that it couldn’t readily be transported en masse.
It would take an enterprising family with a knack for marketing to help the poinsettia realize its full saleable potential.
The ‘poinsettia prince’ and the rise of a monopoly
In 1900, a German immigrant named Albert Ecke packed his bags for Fiji, where he intended to open a health spa.
En route, he made a pitstop in Los Angeles and chose to settle there instead — a decision that would change the trajectory of agricultural history.
Ecke and his family established a dairy farm and a fruit orchard before eventually selling cut flowers, including poinsettias. By 1909, the poinsettias were selling so well that he made them the focus of his entire business.
His son, Paul Ecke, assumed the business in the 1920s and moved the operation to Encinitas, 25 miles north of San Diego.
Ecke soon developed secret breeding techniques that vastly improved the durability and aesthetics of poinsettias.
In the wake of the Plant Patent Act of 1930, which allowed breeders to protect their new cultivars, he registered dozens of his creations, staving off competitors and copycats.
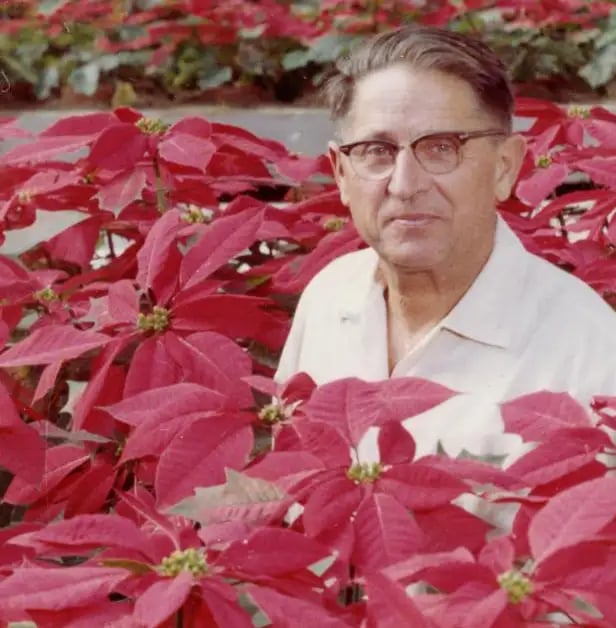

Paul Ecke Sr. with some of his harvest (The Paul Ecke Ranch, Inc. Business Papers and Family Records, via CSU San Marcos archives)
The specifics of Ecke’s prized breeding technique — which he acquired from an amateur German gardener — were guarded with the intensity of the Coca-Cola recipe.
“Nobody at the ranch knew the secret,” his grandson, Paul Ecke III, later told the Los Angeles Times. “My grandfather, my dad, and their breeder knew, and it was done at the breeder’s home so nobody could see.”
The result was a fuller, hardier plant with more branches — a product equipped to endure the tribulations of consumerism.
At the same time, under the leadership of Ecke’s son, Paul Jr., the company marketed the plant as the premier Christmas decoration, sending free samples to women’s magazines and making the rounds on prime-time TV programs like “The Tonight Show.”
By the 1990s, the family was selling 500k+ potted plants, and more than 25m cuttings — baby sections used to produce new plants — to other growers on a royalty basis.
At its peak, the company had a virtual monopoly on the US poinsettia market, maintaining a 90% market share and 150+ patents.
“The Eckes of Southern California are to poinsettias what De Beers of South Africa is to diamonds,” one reporter later proclaimed.
While competitors popped up, none could challenge the exposure, prominence, and rich IP of Ecke Ranch.
That is, until the worst possible scenario came to fruition.
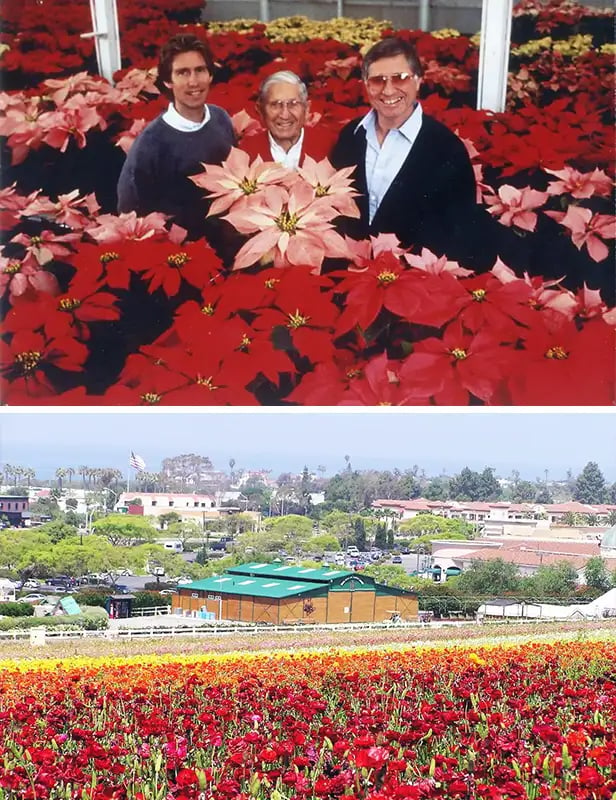

Top: Three generations of the Ecke family (left to right): Paul Ecke III, Paul Ecke Sr., and Paul Ecke Jr. (The Paul Ecke Ranch, Inc. Business Papers and Family Records, via CSU San Marcos archives); Bottom: Paul Ecke Ranch in Encinitas (Tripadvisor)
In 1992, a graduate student named John Dole got his hands on an Ecke cutting and managed to reverse-engineer the company’s top-secret process — a method that involved grafting together 2 poinsettia plants.
His published findings completely upended the poinsettia industry.
“You don’t often see a situation in science where one paper makes a serious impact on the market,” Dole, now an associate dean at North Carolina State University, told The Hustle. “But in this case, it really did.”
Competition flooded in, sparking a “golden age” for poinsettias:
The industry’s main focus shifted from cultivation to breeding, and dozens of new color variations popped up — hues of white, yellow, neon green, and pink — with names like “Premium Picasso” and “Monet Twilight.”
Big-box retailers also began to change the dynamic of the market.
“In the earlier years, poinsettias were mostly sold at independent garden centers and were thought of as an upscale plant,” says Dole. “But when the mass marketers started selling them, that perception changed.”
Home Depot, Lowes, and Walmart began purchasing vast quantities of poinsettias and selling them as loss leaders for as little as $0.99 each.
Zachary Crockett / The Hustle
These changes pressured growers to ruthlessly cut overhead expenses to compete, eventually ushering in an era of consolidation. Giant agriculture firms snatched up smaller outfits and shifted production overseas.
After slowly watching its monopoly decline, Ecke — the one-time king of poinsettias — sold its business to a Dutch conglomerate in 2012.
It marked the end of an era — and the beginning of a new, highly complex, international pipeline.
The modern economics of poinsettias
Today, Ecke is owned by Dümmen Orange, one of the largest plant breeders in the world.
Rebecca Siemonsma, who worked at Ecke from 2004-2012 and now oversees Dümmen’s poinsettia operations, tells The Hustle that the company sells around 50m of the plants each year — more than half of the world’s supply.
In other words, it’s likely that the poinsettias you see at your local Home Depot come from Dümmen.
The journey of a poinsettia plant looks something like so:

Zachary Crockett / The Hustle
According to Dole, the horticulture professor, soil regulations prevent the importation of potted poinsettias. Only cuttings are permitted — so the final stages of growing still happen in the US at major greenhouses.
Cuttings only sell for ~$0.30 each, but large firms like Dümmen make money by selling millions of them at a time.
“Poinsettias are a low-margin, high-volume business,” says Siemonsma. “They’ve become somewhat of an inexpensive commodity in the horticulture industry. But on a unit basis, they’re still near the top.”
This can make the economics a bit tricky for growers.
For most growers, poinsettias aren’t a huge money maker; they’re usually thrown into the mix for several practical reasons:
- They’re the rare plant that can be grown during the late summer months, and they allow growers to mitigate some of their fixed overhead costs during an otherwise stagnant season.
- They allow growers to keep labor employed year-round, rather than just during the busy spring months.
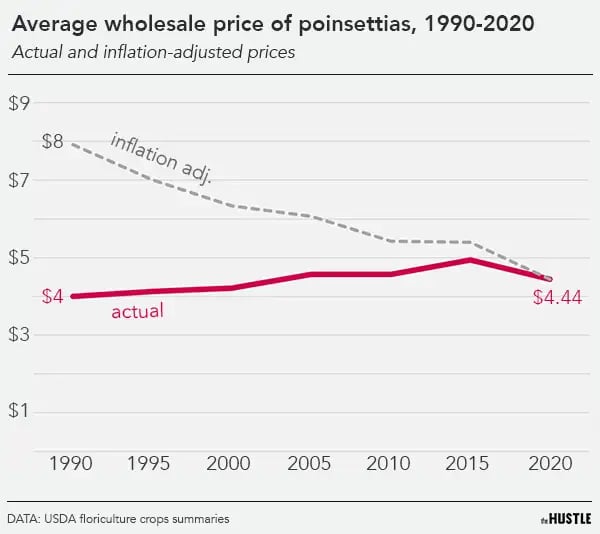
Average wholesale prices for poinsettias have remained stagnant for several decades. Adjusted for inflation, they’ve declined considerably.
Zachary Crockett / The Hustle
But poinsettias have remained lucrative for some.
Wenke Greenhouses is one of the 30 largest greenhouse operations in the US, with several million square feet of crops in Michigan and Georgia.
The company started growing poinsettias in the mid-’80s. Today, it produces ~200k annually, which are sold wholesale to Walmart, Lowes, churches, and fundraisers.
“We’ve had 2 great years,” says Lorence Wenke, the company’s long-time owner, who recently passed the business on to his daughter. “People are staying indoors and plants are thriving across the board.”
Kevin Koeppler is the general manager at Sunbelt Greenhouses, a subsidiary of Wenke Greenhouses based in Douglas, Georgia, where the poinsettias are grown.
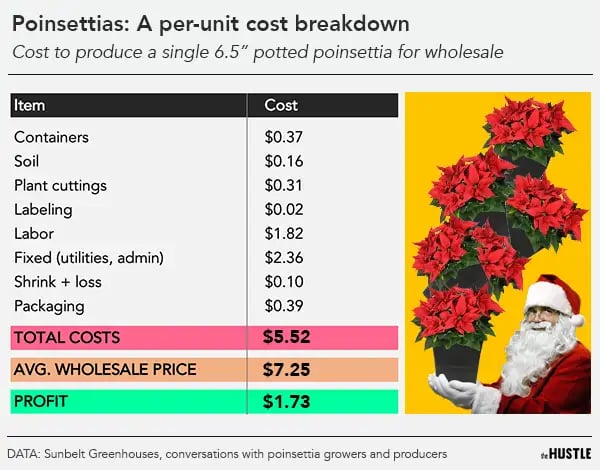
In a large spreadsheet shared with The Hustle, he broke down what the poinsettia sector of the business looks like on the back end:
Zachary Crockett / The Hustle
Those are far better margins than most in the business — but Koeppler says there are a myriad of things that can go wrong along the way.
“There are always a few unexpected things that come up in agriculture,” he says. “One pest infestation might set you back $60k and wipe out most of your margins.”
COVID and ongoing supply chain issues have also put a dent in Koeppler’s usual process.
For instance, he used to import coconut coir — the fibrous coconut husks inside shells — from Indonesia to mix into his soil. But in recent years, he’s had to ditch it because shipping costs have ballooned from $2.1k to $21k per container.

A fresh crop of poinsettias at Sunbelt Greenhouses in Douglas, Georgia (Sunbelt Greenhouses)
One faction who feels they’ve been left out to dry in this booming poinsettia market is Mexican growers.
Though Mexico sells ~$12m worth of poinsettia cuttings to the US market every year, a century-old foreign soil restriction prevents the country from selling its own native plant in potted form to US consumers. The Mexican Embassy has lobbied to change these restrictions with no luck.
Some growers feel embittered that a plant with deep native roots is now patented and controlled by foreign entities: Today, across the border, poinsettismo is used as a derogatory term to describe a person who is arrogant and intrusive.
But on US soil, the market — and the name — isn’t likely to change.
“Nothing says it’s Christmas time like a poinsettia,” says Wenke. “And I think it’ll be that way for a long time.”

